Introduction
The field of mechanical engineering and automation technology is rife with various components that make up larger, more complex systems. One such fundamental component is the Linear Module. In this article, we delve into the understanding of what a Linear Module is, its historic development and the critical role it plays in modern machinery.
This comprehensive guide aims to offer detailed insights into Linear Modules, explaining their principles, types, applications and future trends. We hope to provide both beginners and seasoned professionals with valuable information about these essential components.
Definition of a Linear Module
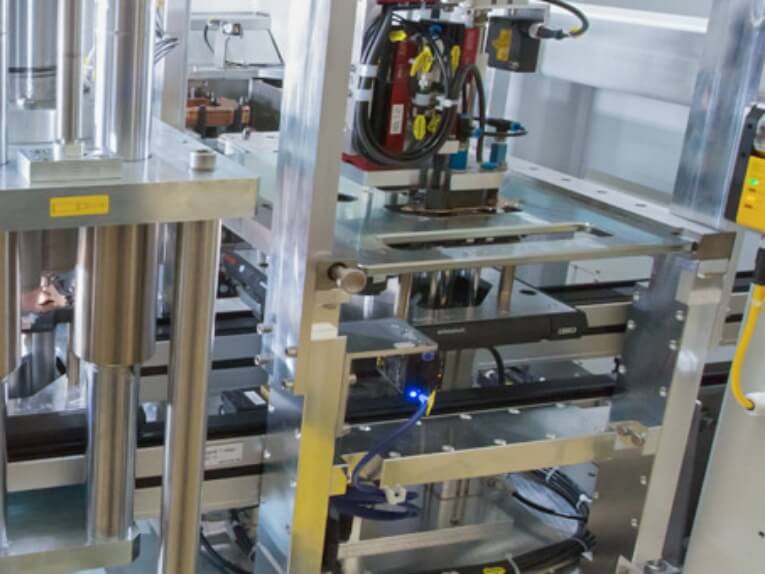
In the simplest terms, a Linear Module is a moving component of a machine or system that operates in a straight line. It is commonly used in industrial automation and precision machinery, transforming rotary motion into linear motion.
Structure of a Linear Module - A Linear Module typically comprises a linear guide, a drive mechanism (like a ballscrew or a belt), and a base structure. The specific type of Linear Module depends on its intended application and the precision required.
Brief History and Evolution
The conception of Linear Modules can be traced back to the early days of automation, where the need for efficient, precise linear movement in machinery was recognized. Over the years, advancements in technology have led to more sophisticated, compact, and efficient Linear Modules.
Emergence of Linear Modules - In the early stages of industrial automation, simple levers and pulley systems were used for linear motion. As technology evolved, so did the systems, leading to the development of the first Linear Modules.
Evolution and Technological Advancements
With the ongoing advancements in materials science, computer technology and precision engineering, Linear Modules have significantly evolved. They’ve become more efficient, reliable, and capable of handling a wider range of tasks in various fields like robotics, medical equipment, and many others.
Concepts Related to Linear Modules
In order to fully comprehend Linear Modules, there are some key concepts that must be understood. These include the principles of Linear Algebra, which provide the mathematical foundation for Linear Modules and the concept of Modularity in engineering.
Prerequisites to Understanding Linear Modules – Linear Modules may appear complex at first glance, but with a basic understanding of related concepts such as Linear Algebra and Modularity in Engineering, they become much more accessible.
Exploring Linear Algebra
Linear Algebra is a branch of mathematics that studies vectors, vector spaces (also called linear spaces), and linear transformations between these spaces. It includes the study of lines, planes, and subspaces, but is also concerned with properties common to all vector spaces.
Role of Linear Algebra in Linear Modules – In the context of Linear Modules, Linear Algebra is crucial as it provides a mathematical framework for describing the linear motion that these modules are designed to perform. Understanding the concepts of vectors and transformations can help engineers design more efficient and effective Linear Modules.
Importance of Modularity in Engineering
Modularity in engineering refers to the design approach that subdivides a system into smaller parts (modules) that can be independently created, modified, replaced, or exchanged with other modules.
Modularity and Linear Modules – In relation to Linear Modules, modularity provides numerous benefits. This reduces downtime and facilitates easier maintenance, making modular systems more cost-effective in the long run.
Post time: Jan-26-2026