Applications of Linear Modules
Key sectors include Industrial Automation, Robotics, and Precision Instrumentation.
Versatility of Linear Modules - The versatility of Linear Modules comes from their varied types and the range of customization options, making them suitable for different applications requiring linear motion.
1. Industrial Automation
In the realm of Industrial Automation, Linear Modules play a pivotal role in various automated machinery and processes, contributing to improved efficiency, precision, and productivity.
Role of Linear Modules in Industrial Automation - They facilitate precise movement and positioning of parts, ensuring accurate and reliable operation of automated systems.
2. Robotics
In Robotics, Linear Modules are integral components, enabling robots to perform precise linear movements, essential for tasks such as assembly, picking and placing, and welding.
Role of Linear Modules in Robotics - Whether in industrial robots, medical robots, or even service robots, Linear Modules contribute to precise motion control, allowing robots to perform their tasks accurately and reliably.
3. Precision Instrumentation
In Precision Instrumentation, such as in medical devices, microscopes, and laboratory automation, Linear Modules provide the necessary precise linear motion.
Role of Linear Modules in Precision Instrumentation – The high precision and efficiency of Linear Modules make them ideal for instruments and devices that require exact positioning or movement, thereby ensuring accurate results and reliable performance.
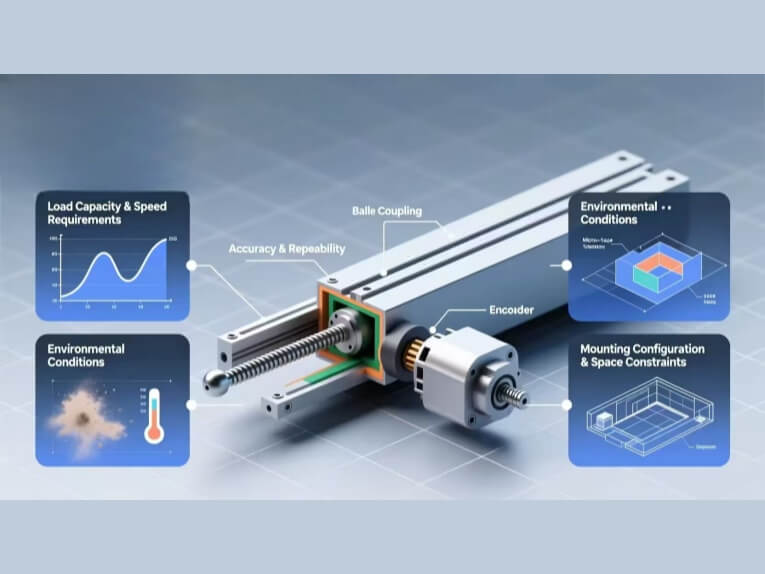
Selection Criteria for Linear Modules
Choosing the right Linear Module for a specific application is critical to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
The Importance of Correct Selection – Conversely, an incorrect choice may lead to suboptimal performance, increased maintenance, and even system failure.
1. Factors to Consider
These include the required precision, speed, load capacity, travel distance, and environmental conditions.
Precision – The required precision of the Linear Module will greatly influence the type of module selected.
Speed and Load Capacity - The required speed and load capacity will also play a significant role in the selection. Belt Driven Modules are generally faster but have lower load capacity, while Ball Screw Driven Modules can handle higher loads but are typically slower.
Travel Distance and Environmental Conditions - Travel distance can influence the choice of Linear Module, as can the operating environment. Longer travel distances may favor Belt Driven Modules, while harsh environmental conditions may require more robust and sealed systems.
2. Common Mistakes in Selection
Common mistakes in selecting Linear Modules often relate to neglecting or misjudging the aforementioned factors.
Overlooking Factors – Overlooking important factors like speed, load, and precision requirements can lead to selecting a Linear Module that’s ill-suited for the application, resulting in poor performance or increased wear and tear.
Over-specification - Another common mistake is over-specification, i.e., selecting a Linear Module that far exceeds the application’s requirements. This often results in unnecessary costs, both in terms of initial purchase and ongoing maintenance.
Post time: Feb-13-2026